Lesson Plans
Selma & Voting Rights: Standing Up for Equality
Through inquiry into primary sources, students discover a story of citizens shaping and sustaining our democracy through civic action and will contemplate the import and impact of citizens who strive for equality. This lesson may be used prior to reading a fictional work or poem related to the civil rights movement or in conjunction with a close reading of Lyndon B. Johnson’s March 15, 1965 voting rights address to Congress (in whole or in part).
The Meaning of the Federalist Papers
This lesson explores the Federalist Papers. In Part I, students engage in a discussion about how they get information about current issues. Next, they read a short background of the Federalist Papers and work individually or in pairs to closely examine the text. In Part II, student pairs analyze excerpts from the Federalist Papers and relate these documents to what they have already learned. In Part III, students work in small groups to research a Federalist or Anti-Federalist and role-play this person in a classroom debate.
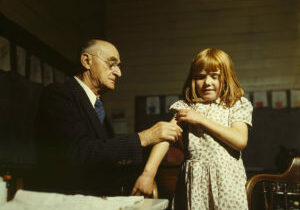
Mandatory Vaccinations: Yea or Nay?
In this three-part lesson students discuss the proper role of government in making public health decisions. In Part I, students discuss their prior knowledge of vaccinations and the purpose of vaccinations. In Part II, students assume the roles of members of Congress to determine if they will vote on a bill to require parents to vaccinate their children. Students will use primary sources to explore the issue, then will work in small groups to discuss both sides of the argument. Finally, students will state and support their vote for or against the bill. In Part III, students conduct independent research in order write their answer to the Essential Question.
Vaccinations, Science, and the Law
In this two-part lesson students explain the role of science in informing public policy. In Part I, students discuss their prior knowledge of vaccinations and the purpose of vaccinations. In Part II, students assume the roles of members of Congress to determine if they will support a bill to require the federal government to compare the health outcomes of vaccinated and unvaccinated children. Students use primary sources to explore the issue and then will work in small groups to discuss the most important factors affecting Congress’s decision. Finally, students interview an adult about their knowledge and opinion of science and public policy, particularly related to vaccinations.
TB or Not TB: Disease Prevention
In this lesson, students use the example of tuberculosis to learn how scientists, the government, and public-interest organizations work together to ensure that the public has equal access to disease-prevention information and support. In Part I, students discuss the role of science in public health and play the role of “Disease Detectives” to learn more about tuberculosis from primary sources. In Part II, students participate in a gallery walk to analyze historic public health posters about disease prevention to learn about the people and groups responsible for fighting tuberculosis. In Part III, student groups apply what they have learned to create their own posters about disease prevention today.
Gerrymandering: Voting by Numbers
Students learn about the application of ratios and proportions to the real political issue of gerrymandering. In Part I, students conduct a primary-source analysis of the original 1812 political cartoon about Elbridge Gerry’s redistricting in Massachusetts to build background knowledge. In Part II, students analyze a historical map of Massachusetts’s gerrymandered voting districts in 1812 and compare it to the political cartoon to discuss issues of fairness. In Part III, students solve a hypothetical problem about fair representation on a student council, using their knowledge and understanding of gerrymandering and ratios. Finally, students role-play state legislators in a hypothetical state to solve problems of representation, including gerrymandering.
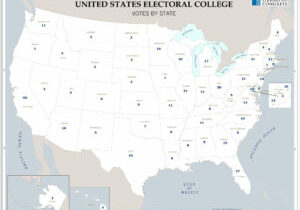
Electoral College: Are All Votes Equal?
Students examine the process of voting and the Electoral College. Applying mathematical percentages, students experience how population and voting impact elections in this country and consider if everyone’s vote matters. Then students consider the use of the Electoral College and how it aligns with the popular vote.